Main Article Content
Abstract
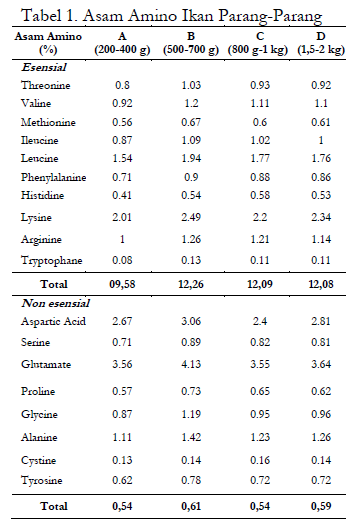
Wolf herring fish (Chirocentrus dorab) is one of the marine fisheries commodities that can be processed into processed products rich in nutrients. One of the factors that influences the chemical composition of fish and processed products is the weight of the fish used. The research aimed to determine the chemical characteristics of wolf herring fish based on differences in weight. The weights of fish used were 200-400 g, 500-700 g, 800-1 kg, and 1.5-2 kg. The research parameters were analysis of the water content, protein, fat, ash, amino acids, and fatty acids. The results showed that the proximate value showed an increase along with increasing fish weight. Amino acid analysis of the four fish weights showed that the highest concentration of essential amino acids was lysine, while the non-essential amino acid was glutamate. Identifying fatty acids showed that the saturated fatty acid with the highest quantity was palmitic acid, while the unsaturated fatty acid was docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Wolf herring fish weighing between 800 grams and 1 kilogram have optimal chemical characteristics. Their nutrient composition includes 20.78% protein, 1.85% fat, 55.07% unsaturated fatty acids, and 12.09% essential amino acids. Research indicates that fish weight affects their chemical properties, especially fatty acid content.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.